Java
Java is an object-oriented language similar to C++, but simplified to eliminate language features that cause common programming errors. Java source code files (files with a .java extension) are compiled into a format called bytecode (files with a .class extension), which can then be executed by a Java interpreter.
Compiled Java code can run on most computers because Java interpreters and runtime environments, known as Java Virtual Machines (VMs), exist for most operating systems, including UNIX, the Macintosh OS, and Windows. Bytecode can also be converted directly into machine language instructions by a just-in-time compiler (JIT).
Java presentation tier, Business Logic teir, Data Teir

J2EE
- At the client tier, J2EE supports pure HTML, as well as Java applets or applications. It relies on Java Server Pages and servlet code to create HTML or other formatted data for the client.
- Enterprise JavaBeans (EJBs) provide another layer where the platform's logic is stored. An EJB server provides functions such as threading, concurrency, security and memory management. These services are transparent to the author.
- Java Database Connectivity (JDBC), which is the Java equivalent to ODBC, is the standard interface for Java databases.
- The Java servlet API enhances consistency for developers without requiring a graphical user interface.
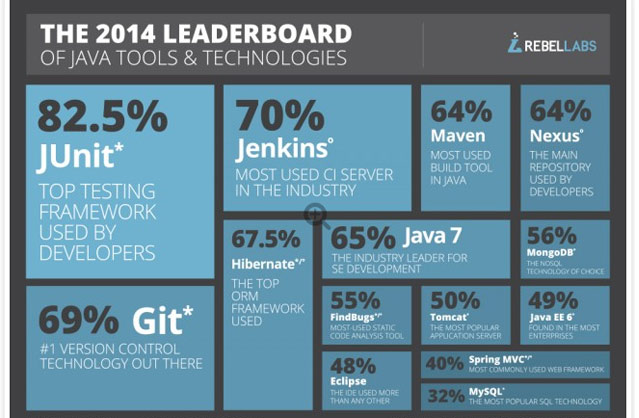
IDEs vs. Build Tools
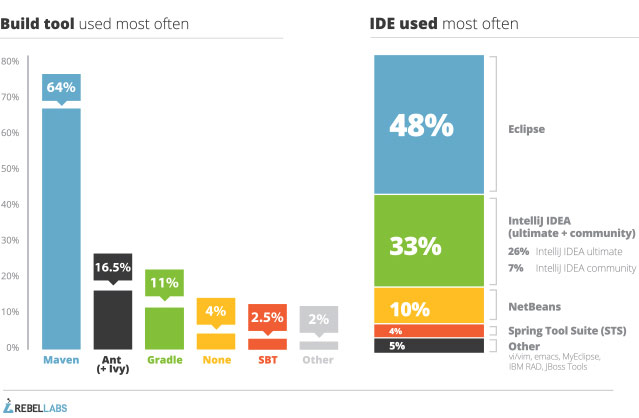
Popular Java Web Frameworks
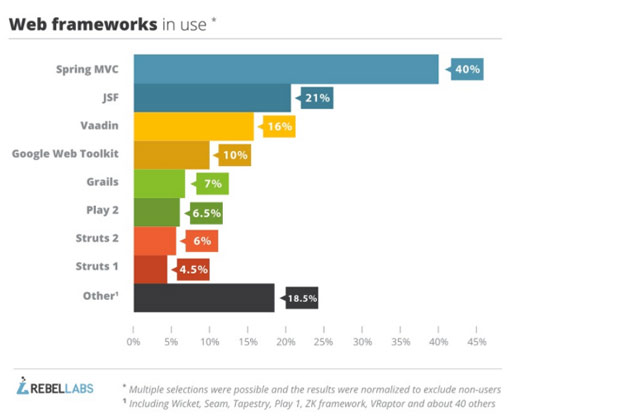
Java Tools & Technologies 2014